Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hidaka, Akihide
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332, p.1607 - 1623, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide
Nuclear Technology, 208(2), p.318 - 334, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The author previously proposed that the Cs bearing microparticle (Type A) may have been formed by melting and atomization of glass fibers (GF) of the HEPA filter in the SGTS due to flame and blast during the hydrogen explosion in Unit 3. If this hypothesis is correct, the Type A could contain or accompany carbon (C), that ignites spontaneously above 623 K, because of the limited time to be heated up, inclusion of C in the binder applied on the GF surface and closely located charcoal filter. As the previous studies did not focus on C, the present analyses were performed with EPMA whether the Type A contains C. The results showed that the Type A contained C originating from the binder, and non-spherical particles accompanied by the Type A and the film surrounding the Type A contained more C, which is thought to originate from the charcoal filter. These results cannot be explained by the other mechanisms proposed so far, and can be explained consistently by the author proposed hypothesis.
Hidaka, Akihide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.831 - 841, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:80.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)The insoluble Cs particles (Type A) were firstly observed in Tsukuba-city on the morning of March 15. The particles have been considered to be generated in RPV of Unit 2 by evaporation/condensation based on the measured  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio and the core temperatures of each unit. However, the Type A particles with smaller diameter than the Type B particles of Unit 1 origin, are covered by almost pure silicate glass and have a trace of the quenching. This indicates that the particles could have been generated due to the melting of the HEPA filter in SGTS by the fire of H
Cs ratio and the core temperatures of each unit. However, the Type A particles with smaller diameter than the Type B particles of Unit 1 origin, are covered by almost pure silicate glass and have a trace of the quenching. This indicates that the particles could have been generated due to the melting of the HEPA filter in SGTS by the fire of H detonation at Unit 3, and atomization followed by quenching of the molten materials by air blast of the explosion. Although the particles were mostly dispersed to the sea because of the wind direction, some of them deposited onto the lower elevation of R/B at Unit 3, could have been subsequently re-suspended and released into the environment, by the steam flow in the R/B caused by restart of the Unit 3 core cooling water injection at 2:30 of March 15.
detonation at Unit 3, and atomization followed by quenching of the molten materials by air blast of the explosion. Although the particles were mostly dispersed to the sea because of the wind direction, some of them deposited onto the lower elevation of R/B at Unit 3, could have been subsequently re-suspended and released into the environment, by the steam flow in the R/B caused by restart of the Unit 3 core cooling water injection at 2:30 of March 15.
Hotta, Akitoshi*; Morita, Akinobu*; Kajimoto, Mitsuhiro*; Maruyama, Yu
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(3), p.139 - 152, 2017/09
Kinuhata, Hiroshi*; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Kodama, Takashi*; Tamauchi, Yoshikazu*; Shibata, Yuki*; Anzai, Kiyoshi*; Matsuoka, Shingo*
Nuclear Technology, 192(2), p.155 - 159, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experiments using a small-scale apparatus with 30 ml actual high-level liquid waste from the Tokai Reprocessing Plant were carried out to show that the hydrogen concentration in the gas phase reaches a steady-state value of much less than 4% (lower explosive limit) in the absence of sweeping-air. The H concentration reached a steady-state value as was expected and it was compared with a value predicted from an equation with parameters which had been obtained using the simulated solution. Satisfactory agreement showed that the Pd-ion catalytic H
concentration reached a steady-state value as was expected and it was compared with a value predicted from an equation with parameters which had been obtained using the simulated solution. Satisfactory agreement showed that the Pd-ion catalytic H consumption reaction previously found in the simulated solution proceeded equally well in the actual solution.
consumption reaction previously found in the simulated solution proceeded equally well in the actual solution.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 236(19-21), p.2010 - 2025, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A computer code JASMINE-pre was developed for the prediction of premixing conditions of fuel-coolant interactions and the debris bed formation behavior relevant to severe accidents of light water reactors. JASMINE-pre consists of three melt component models: melt jet, melt particles and melt pool, coupled with a two-phase flow model derived from the ACE-3D code developed at JAERI. Simulations of the FARO corium quenching experiments with a saturated water pool and with a subcooled water pool were performed with JASMINE-pre and 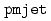 . JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
. JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
Chiba, Atsuya; Saito, Yuichi; Narumi, Kazumasa
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.343 - 345, 2006/01
Recently, we have gained interesting results on the interaction between a swift cluster ion and a solid in TIARA. For the elucidation of these interactions and the physical effects, it is very important to grasp the structure of the cluster. For this purpose, a measurement system based on Coulomb explosion imaging (ECI) for analyzing the structure of small carbon clusters has been developed. The ECI technique involves the foil-induced dissociation of a swift cluster by electron stripping. As our first step of the investigation on the carbon cluster structure, the preliminary experiment was carried out on the structure dependence on the average charge state of atoms that composed a cluster passing through a thin foil.The result shows the same tendency as a calculated theoretical value.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Usami, Tsutomu*; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2005-017, 173 Pages, 2005/08
A series of experiments on the break-up of high temperature oxide and steel melt jets in a water pool was conducted. The objective was to obtain data for the jet break-up length and size distribution of the droplets produced by the jet break-up, and information on the influence of material properties. Also, we tried to obtain additional information giving a clue to the mechanism governing the melt jet break-up, such as flow intensity of the steam column surrounding the melt jet, and its relation with the droplet size. In the experiments, zirconia-alumina mixture and stainless steel melt jets with diameter  17mm and velocity
17mm and velocity  7.8m/s at the water surface were dropped into a deep (2.1m) or shallow (0.6m) water pool with various subcool. From the results of the present experiments and also by referring other experimental data from literature, we obtained empirical correlation equations for the jet break-up length, the fraction of jet broken-up in a shallow pool where the jet was not completely broken-up, and the droplet size.
7.8m/s at the water surface were dropped into a deep (2.1m) or shallow (0.6m) water pool with various subcool. From the results of the present experiments and also by referring other experimental data from literature, we obtained empirical correlation equations for the jet break-up length, the fraction of jet broken-up in a shallow pool where the jet was not completely broken-up, and the droplet size.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nishihara, Tetsuo
JAERI-Tech 2005-033, 206 Pages, 2005/07
In this report, we investigated the effects of jet for the dispersion and explosion analysis of leaked gas, obstacles, position of an ignition point and cell size for the gas explosion analysis, and atmospheric stability for the dispersion analysis of the leaked gas, with PHOENICS, AutoReaGas, and AUTODYN. Then, we carried out two accident analyses about combustible fluid leakage based on the investigation results of these effects. As a result, it was shown that important buildings related to safety was hardly affected by the explosion of the leaked gas.
Chiba, Atsuya; Saito, Yuichi; Tajima, Satoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 232(1-4), p.32 - 36, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)The structure of cluster ion may be important parameter for resolution of physical effect and interaction with cluster ion and solid. In this paper, we report a Coulomb explosion imaging of the constituent atoms of a swift carbon cluster (Cn, n=2, 3 and 6) passing through a thin foil and their average charge state that related with the structure of the cluster. The experimental setup is based on the 3MV TANDEM accelerator at the JAERI Takasaki. The cluster ion beam is pulsed by electrical deflection plates and an aperture. A few clusters pass trough the thin foil during 1 second, and the resulting are collected by the luminance plate detector. The average charge state was shown an almost same tendency as calculate theoretical value.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2005/05
The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions were evaluated for a BWR Mk-II model plant. The evaluation was made for two scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area, or in the suppression pool. A probabilistic approach, Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS), was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The fragility curves connecting the steam explosion loads and containment failure were developed based on simplified assumptions on the containment failure scenarios. The mean conditional probabilities of containment failure per occurrence of a steam explosion were 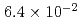 for suppression pool and
for suppression pool and 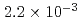 for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics, Operations and Safety (NUTHOS-6) (CD-ROM), 18 Pages, 2004/10
A steam explosion simulation code JASMINE is under development at JAERI for the assessment of steam explosion impacts on the integrity of containment vessel during severe accidents in light water reactors. Selected alumina and corium steam explosion experiments, KROTOS-44, 42, 37 and FARO-L33 were simulated with JASMINE code. The experimentally observed difference of the steam explosion intensity with the two materials, alumina and corium, was reproduced in the simulations without changing the model parameters related to the fine fragmentation process, but based on the difference in the premixing behavior predicted by the simulations. The simulation of corium experiments showed more fraction of the melt droplets frozen during premixing, as well as more void fraction, and those two points were likely to be the primary reasons of weak interactions in corium experiments.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Groethe, M. A.*; Nitta, Yoshikazu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 232(1), p.111 - 119, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is important to grasp the explosion characteristics of object gases: natural gas and methane, in order to evaluate the influence of a gas explosion accident in the HTTR hydrogen production system on the reactor. Thus, we carried out explosion experiments of the object gases in semi-open space, and verified a numerical analysis code for the simulation of the explosion accident. It was confirmed that NG-air mixture or methane-air mixture in semi-open space didn't result in DDT although 10 g of C-4 explosive was used as an ignition source, and the numerical results agreed relatively with the experimental results. As a result, we could have the prospects for predicting the influence of the explosion accident on the reactor.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Nitta, Yoshikazu*
Nuclear Technology, 146(1), p.49 - 57, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)One of the most important safety design issues for a hydrogen production system coupling with a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is to ensure reactor safety against fire and explosion accidents because a large amount of combustible fluid is dealt with in the system. The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) has a demonstration test plan of a hydrogen production system by steam reforming of methane coupling with the High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). In the plan, we developed the P2A code system to analyze event sequences and consequences in detail on the fire and explosion accidents assumed in the HTGR or HTTR hydrogen production system. This paper described the three accident scenarios assumed in the system, the structure of P2A, the analysis procedure with P2A and the results of the numerical analyses based on the accident scenarios, and it was showed that P2A was a useful tool for the accident analysis in the system.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu*; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2002-021, 36 Pages, 2002/11
Silicon is a material which is easily oxidized like zirconium which is one of the LWR core materials. Also, its steam explosion behavior is a concern in semi-conductor industries where its melt is handled. In this study, steam explosion behavior of silicon melt and contribution of oxidation reaction in a steam explosion were investigated. Two cases of experiments were performed by dropping silicon melt into a water pool and both produced spontaneous steam explosions. Energy conversion ratio was 4--9% which was similar or slightly larger compared with previous experiments with thermite melt. Fragmentation of the melt was finer than previous experiments and the mass median diameter of the debris was 65--85 m. An oxide layer of about 5
m. An oxide layer of about 5 m thick was fond on the debris surface indicating possibility of oxidation of several % of the melt.
m thick was fond on the debris surface indicating possibility of oxidation of several % of the melt.
Maruyama, Yu*; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(8), p.854 - 864, 2002/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Moriyama, Koichi*; Nakamura, Masashi*
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-014, 255 Pages, 2002/07
One of the most important safety design issues for an HTGR hydrogen production system is to ensure reactor safety against fire and explosion accidents in the hydrogen production plant because a large amount of combustible fluid is dealt with in the system. JAERI has the demonstration test plan to connect the hydrogen production system with the HTTR. In the plan, we considered effective measures against the fire and explosion accidents in the HTTR hydrogen production system, which were applicable to the HTGR hydrogen production system of a commercial base, and also developed the P2A code system to analyze event sequences and consequences in detail, on assumed fire and explosion accidents in the HTGR hydrogen production system and the HTTR hydrogen production system. The P2A can analyze the process of leakage, dispersion, ignition, and combustion including deflagration and detonation of the combustible fluid in the internal and external area of the reactor building. In this report, we describe the outline and the usage of the P2A, and the results of preliminary calculations.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Hirano, Masashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-8-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.209 - 214, 2002/06
Through a review of experimental works on steam explosions and consideration on the uncertainty in the methodology for plant scale analysis of each stage of the phenomena, it was identified that the molten jet breakup process in premixing has an important uncertainty caused by lack of experimental knowledge. Based on this perspective, an experimental work are under planning at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), in which the premixing stage of steam explosions in a deep water pool is modeled by high temperature oxide melts. Melt material and scale of the experiment were examined in terms of the simulation capability of the jet breakup mechanism in a plant scale phenomena. Materials and geometrical scale considered adequate were found.
 -scaling of lattice parameter change in high ion-velocity region (
-scaling of lattice parameter change in high ion-velocity region (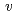
 2.6
2.6 10
10 cm/s) in ion-irradiated EuBa
cm/s) in ion-irradiated EuBa Cu
Cu O
O
Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Michikami, Osamu*; Wakana, Hironori*; Hashimoto, Takeo*; Kambara, Tadashi*; M ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*
ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 193(1-4), p.278 - 282, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.9(Instruments & Instrumentation)Swift heavy ions with wide energy range of 80MeV-3.84GeV have been irradiated to EuBa Cu
Cu O
O oxide superconductors, and the lattice parameter change due to elecronic excitation has been measured. In the high ion-velocity region, the change in lattice parameter per unit fluence varies as the 4th power of the electronic stopping power. However, in the low-velocity region, the deviation from the 4th power dependence is observed. The results are analyzed by using the primary ionization rate, and it is found that the results support that the Coulomb explosion triggers the atomic displacements.
oxide superconductors, and the lattice parameter change due to elecronic excitation has been measured. In the high ion-velocity region, the change in lattice parameter per unit fluence varies as the 4th power of the electronic stopping power. However, in the low-velocity region, the deviation from the 4th power dependence is observed. The results are analyzed by using the primary ionization rate, and it is found that the results support that the Coulomb explosion triggers the atomic displacements.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 14th Hydrogen Energy Conference (WHEC 2002) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2002/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) has the demonstration test plan to connect a hydrogen production system by steam reforming of methane with the High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). One of the most important safety design issues for the HTTR hydrogen production system is to ensure reactor safety against fire and explosion accidents. Therefore, we developed the P2A code system to analyze event sequences and consequences in detail, on assumed fire and explosion accidents in the HTTR hydrogen production system. It is possible that the P2A analyzes the process of leakage, dispersion and combustion including deflagration and detonation of the combustible fluid in the internal and external area of the reactor building. This paper describes the outline of the P2A and the results of preliminary calculations.